Burano
This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2017) |
 View of Burano: Rio Giudecca canal, colorful houses and the leaning campanile of San Martino church. | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 45°29′09″N 12°25′03″E / 45.485771°N 12.417487°E |
| Adjacent to | Venetian Lagoon |
| Area | 210,800 m2 (2,269,000 sq ft) |
| Highest elevation | 1 m (3 ft) |
| Administration | |
| Comune | Venice |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 2,777 |
Burano is an island in the Venetian Lagoon, northern Italy, near Torcello at the northern end of the lagoon, known for its lace work and brightly coloured homes. The primary economy is tourism.[1]
Geography
[edit]Burano is 7 kilometres (4 miles) from Venice, a 45-minute trip from St. Mark's Square by vaporetto, a Venetian water bus.
The island is linked to Mazzorbo by a bridge.[2] The current population of Burano is about 2,800.[3] Originally, there were five islands and a fourth canal that was filled to become via e piazza Baldassare Galuppi, joining the former islands of San Martino Destra and San Martino Sinistra.[4]
Burano has historically been subdivided into five sestieri, much like Venice. They correspond to the five original islands. The sixth sestiere is neighboring Mazzorbo:
| Sestiere | Area[5] | Population | Density | Map | |
| San Mauro | 6.8 ha | 818 | 12,029 | 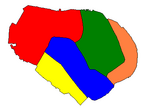 | |
| Giudecca[6] | 2.5 ha | 255 | 10,200 | ||
| San Martino Sinistra | 4.4 ha | 586 | 13,318 | ||
| San Martino Destra | 5.1 ha | 759 | 14,882 | ||
| Terranova | 2.3 ha | 359 | 15,609 | ||
| Burano (Island) | 21.1 ha | 2,777 | 13,176 | ||
| Mazzorbo[7] | 51.8 ha | 329 | 635 |
Burano has a high population density, calculated at more than 13,000 per square kilometer, or more than twenty times the density of neighboring Mazzorbo. It is almost entirely covered by residential buildings, with few small green areas.
History
[edit]

The island was probably settled by the Romans, and in the 6th century was occupied by people from Altino, who named it for one of the gates of their former city. Two stories are attributed to how the city obtained its name. One is that it was initially founded by the Buriana family, and another is that the first settlers of Burano came from the small island of Buranello, about 8 kilometres (5 miles) to the south. [citation needed]
Although the island soon became a thriving settlement, it was administered from Torcello and had none of the privileges of that island or of Murano. It rose in importance only in the 16th century, when women on the island began making lace with needles, being introduced to such a trade via Venetian-ruled Cyprus.[8] When Leonardo da Vinci visited in 1481, he visited the small town of Pano Lefkara and purchased a cloth for the main altar of the Duomo di Milano. The lace was soon exported across Europe, but trade began to decline in the 18th century and the industry did not revive until 1872, when a school of lacemaking was opened.[9] Lacemaking on the island boomed again, but few now make lace in the traditional manner as it is extremely time-consuming and therefore expensive.[10]
Burano has been home to great artists such as the composer Baldassare Galuppi who was born in 1706, the singer-songwriter Pino Donaggio who was born in 1941 and the sculptor Remigio Barbaro who was born in 1911.[11]
Main sights
[edit]Burano is also known for its small, brightly painted houses,[12] which are popular with artists. The colours of the houses follow a specific system, originating from the golden age of its development. If someone wishes to paint their home, one must send a request to the government, who will respond by making notice of the certain colours permitted for that lot.[13] The island is considered among the ten most colorful places in the world.[14]
The heart of the village is Piazza Baldassare Galuppi which is the only square in the village.[15] The Lace Museum, Town Hall, a well made entirely out of Istrian stone and the statue of Baldassare Galuppi made by Remigio Barbaro can also be found in the square.[16]
Other attractions include the church of San Martino, with a leaning campanile and a painting by Giambattista Tiepolo (Crucifixion, 1727), the Oratorio di Santa Barbara and the Museum and School of Lacemaking.[17]
Transport
[edit]The island forms part of the Actv waterbus network. The following lines connect to Burano:
9 (Burano-Torcello)
12 (Fondamente Nove-Murano-Burano-Treporti-Punta Sabbioni)
14 (S.Zaccaria-Lido SME-Punta Sabbioni-Burano)
A night service also operates.
Gallery
[edit]-
Rio della Giudecca
-
Rio di Terranova
-
Rio del Pontinello
-
Nearly all buildings are painted in rich colors
-
View on a canal at dawn
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Academy, Students'. Venice- Queen of the Adriatic. Lulu.com. ISBN 9781435774681.
- ^ Mather, Victoria (26 July 2012). "Discovering an Italian Retreat". Vanity Fair. Retrieved 25 April 2017.
- ^ "Island of Burano | Venezia". www.italiaoutdoors.com. Retrieved 2023-03-21.
- ^ "Island of Burano | Venezia". www.italiaoutdoors.com. Retrieved 2023-03-21.
- ^ Relative area portions measured from map.
- ^ Not to be confused with Giudecca in the sestiere Dorsoduro of the historic center of Venice.
- ^ Neighboring island (not on map).
- ^ "Colorful Burano worth a side trip — by water — from Venice". Tampa Bay Times. 2016-12-14. Retrieved 2019-06-20.
Local women began making lace in the 16th century after merchants brought back needles from Venetian-controlled Cyprus, where the skill already flourished.
- ^ "Burano | Italy | Britannica". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 2023-04-09.
- ^ "Burano | Italy | Britannica". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 2023-04-09.
- ^ "A dive into the past of Burano | Visitvenezia.eu". www.visitvenezia.eu. Retrieved 2023-04-09.
- ^ Christofi, Dora (26 August 2015). "Murano & Burano: The Venetian lagoon Islands". Trip-experiences.com. Retrieved 25 April 2017.
- ^ Strutner, Suzy (5 November 2013). "Burano, Italy Is The Cheeriest Little Island, And It Will Lift Your Soul On Travel Tuesday". Huffington Post. Retrieved 25 April 2017.
- ^ "A dive into the past of Burano | Visitvenezia.eu". www.visitvenezia.eu. Retrieved 2023-04-09.
- ^ e-borghi. "Burano". e-borghi. Retrieved 2023-04-09.
- ^ e-borghi. "Burano". e-borghi. Retrieved 2023-04-09.
- ^ "Venice Lace Museum Official Website". visitmuve.it. Retrieved 25 April 2017.
External links
[edit] Media related to Burano at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Burano at Wikimedia Commons






